3D Drone Mapping and Modeling
Drone Mapping and 3D Modeling
Drone mapping services provided are intended for visual augmentation and should not be used as a substitute for traditional land surveying methods.
- Orthomosaic Maps: These are high-resolution aerial images that have been geometrically corrected (orthorectified) to remove the effects of terrain relief and camera orientation. Orthomosaic maps can be used to create 2D maps or 3D models of an area.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are 3D representations of an area that show the terrain’s elevation. DEMs can be created from aerial imagery or lidar (light detection and ranging) data collected by drones.
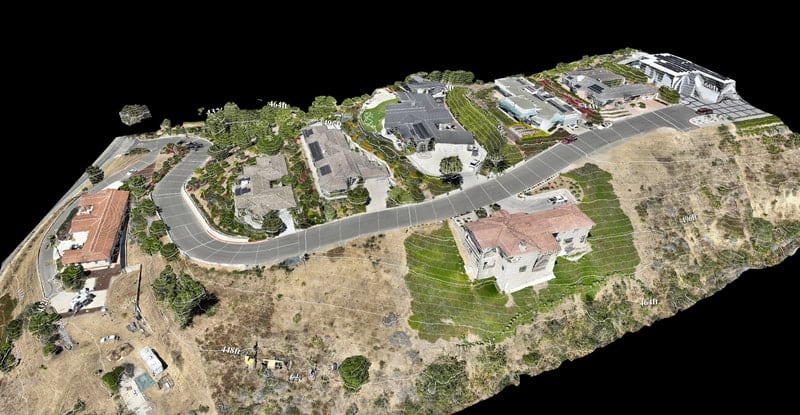
- 3D Models: Drones can be used to create 3D models of buildings, infrastructure, and other features. These models can be used for a variety of purposes, such as asset management, planning, and visualization.
- Videos and Photos: Drones can capture high-resolution videos and photos of an area from a bird’s-eye view. These can be used for documentation, marketing, and other purposes.
- Thermal Imagery: Drones equipped with thermal cameras can capture images that show the temperature of an area or object. This can be useful for identifying problems, such as insulation issues or overheated machinery.





3D Models
3D drone mapping are done with drones equipped with cameras that fly over a target area to capture a series of overlapping images.
These images create 3D models and maps. Through the use of drone 3D modeling, you can get an accurate representation of your building, land, or surveyed spaces.
3D Drone Mapping Services For
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Inspection
- Real Estate
- 3D Asset modeling
- Energy
- Thermal Imaging
Elevation models and Digital Terrain Models
A 3D Elevation Model (DEM) and a Digital Terrain Model (DTM) are digital representations of a terrain’s surface, displaying its elevation and shape in a three-dimensional form. While both models represent the earth’s surface, a DEM includes all surface features like buildings and vegetation, whereas a DTM focuses solely on the natural terrain, excluding these features.
Drones, equipped with cameras or lidar sensors, play a crucial role in creating these models. They fly over targeted areas, capturing images or gathering lidar data that are later processed using specialized software to develop accurate 3D models. The quality and precision of these models depend on various factors, including the resolution and overlap of captured images, the density and accuracy of lidar data, and the drone’s stability.
Factors like atmospheric conditions and moving objects in the area can affect the model’s accuracy. DEMs and DTMs have diverse applications, including the creation of 2D maps, terrain analysis, volume measurement, and virtual tour generation.
- Construction and engineering 3D models and DTMs can be used to plan and monitor construction projects such as roads bridges and buildings.
- Agriculture Drones can be used to create 3D models and DTMs of fields to help with crop management and precision agriculture.
- Environmental management 3D models and DTMs can be used to monitor and analyze changes in land cover and topography such as erosion or land development.
- Disaster response 3D models and DTMs can be used to assess damage and plan recovery efforts after natural disasters such as earthquakes floods and wildfires.
- Mining 3D models and DTMs can be used to plan and monitor mining operations such as the extraction of minerals and the rehabilitation of mine sites.
- Real estate 3D models and DTMs can be used to create virtual tours and marketing materials for real estate properties.
- Military and defense 3D models and DTMs can be used for mission planning and situational awareness in military and defense operations.

Orthomosaic Drone Imaging and Mapping
Orthomosaics are high-resolution aerial images that have been geometrically corrected (orthorectified) to remove the effects of terrain relief and camera orientation.
Orthomosaics provide a detailed, accurate, and up-to-date view of an area, which can be useful for a variety of applications such as mapping, inspection, and monitoring.
Orthomosaics can be used to create 2D maps and 3D models of an area, which can be useful for planning, analysis, and visualization.
They can be used to measure distances, areas, and volumes, which can be useful for asset management, construction, and other applications.
They can be used to identify and analyze features such as roads, buildings, and vegetation, which can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as disaster response, environmental management, and land use planning.
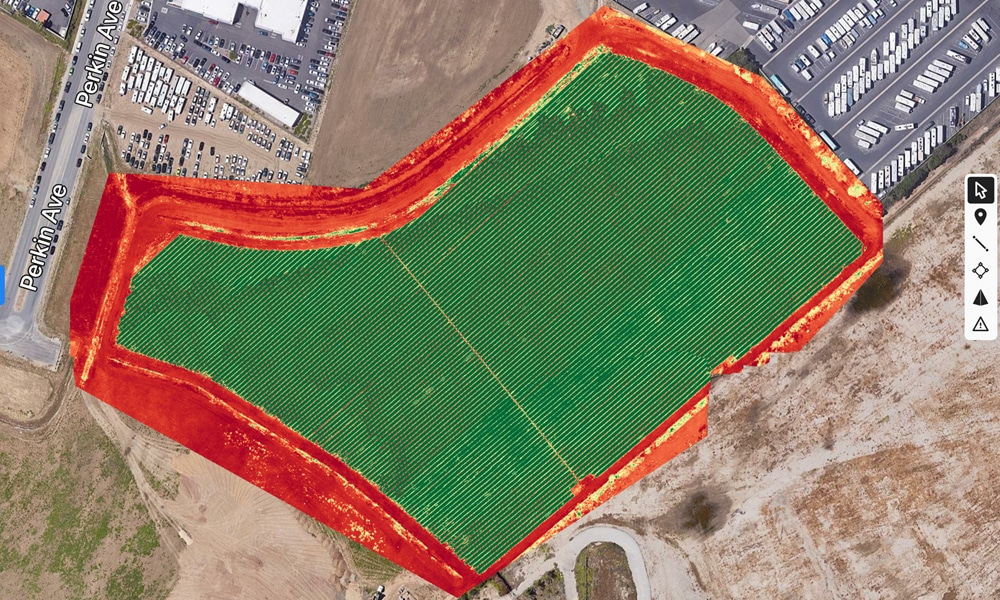
Plant Health NDVI & NIR
The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Near-Infrared (NIR) technologies, utilized in drones, offer a revolutionary approach to assessing plant health. NDVI, a key indicator of chlorophyll presence, leverages the difference between NIR and red bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Drones equipped with specialized cameras can capture both NIR and visible light, generating NDVI maps to pinpoint areas with potentially unhealthy plants. This empowers farmers to fine-tune their agricultural practices, including irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
NDVI maps offer a spatially precise, real-time overview of crop health across vast areas. This method is better than traditional ground-based observation in both scale and accuracy, allowing for targeted interventions in agriculture. Its applications extend from precision farming, where resources are allocated efficiently based on crop health, to yield prediction, offering insights into potential harvest outcomes.
By integrating NDVI data with other agricultural technologies, farmers can achieve a comprehensive understanding of their crops, leading to optimized yields and sustainable farming practices.

